Dalia Savy
Kanya Shah
AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
Separating Solutions into Solute and Solvent
When dealing with solutions, you will have a solute (or multiple solutes) dissolved in a solvent. Many times, a chemist will need to separate these solutions, especially after a chemical reaction has taken place.
There are many methods by which this can occur:
Evaporation
Evaporation is a process by which a solvent is boiled and thus evaporated in order to separate out the solute. For example, if you boil salt water🌊 long enough, you will be left with a small amount of salt🧂 at the bottom of your pot.
The same idea applies to essentially any solution with a solid, soluble solute. Evaporation is the simplest kind of separation and is often the one most students have the most experience with and understand the easiest. Essentially, just boil part away!

Image Courtesy of eschooltoday.com
Filtration
Filtration is also a simple one to understand. When filtering a mixture, one runs the mixture through a porous barrier. With this barrier, the liquid passes through, but the solid remains in the filter. A good real life example of filtration is when making coffee, you pour the mixture of coffee beans and hot water through a coffee filter to let the coffee run through into your mug, but the ground coffee beans stay behind.
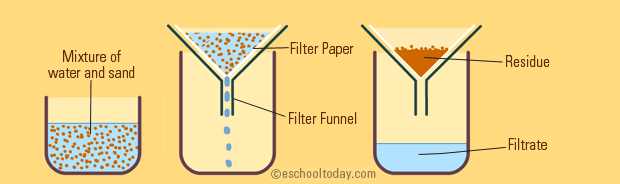
Image Courtesy of eschooltoday.com
Imagine you are filtering a solution of salt, water, and sand. Can you guess what will get caught up in the filter paper? ONLY the sand will. This is because the salt will dissolve in the water since it is not insoluble.
Only insoluble substances will be filtered with filtration. The filtrate would then be both salt and water, or salt water. Therefore, filtration isn't effective if you want to fully separate all of these elements. After filtering the sand out, you would have to evaporate the salt water solution to separate the salt.
Chromatography
Chromatography is a process used to separate solutions of multiple liquids by using an absorbent solid like paper and an "appropriate liquid", typically a non-polar solvent, but a solvent like water is also possible. Paper chromatography has this solvent travelling up the paper and essentially "dragging" each part of the solution away from itself via differences in intermolecular forces.
💡Remember - Like dissolves like. If the paper is nonpolar, the most nonpolar substance / least polar substance will travel the farthest up the paper.
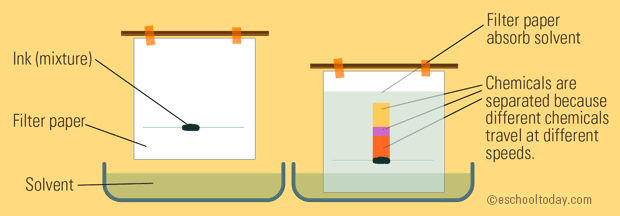
Image Courtesy of eschooltoday.com
Distillation
Distillation, like chromatography, is used to separate solutions of liquids. With distillation, the fact that different liquids have different boiling points is taken advantage of. Through distillation, a solution is carefully heated such that only one liquid boils out and then recondenses into another beaker. The first liquid to boil is the one with the weakest IMFs, and it increases as boiling point increases. This traditional form of distillation is called fractional distillation.
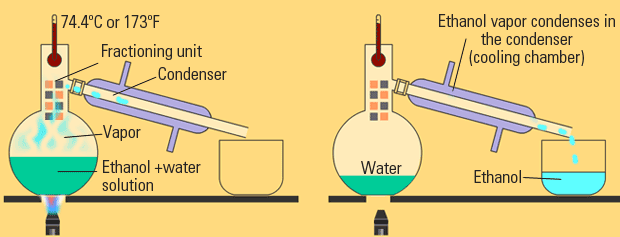
Image Courtesy of eschooltoday.com
Distillation can also be used to recollect the liquid in an evaporation separation. This is called simple distillation.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
✍️Free Response Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.