Unit 8 Overview: 20th-Century Global Conflicts
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Eric Beckman
Isabela Padilha
AP European History 🇪🇺
335 resourcesSee Units
Unit 8: 20th-Century Global Conflicts
Welcome to Unit 8. This Unit includes important events from the first half of the 20th Century. Not surprisingly, trends from the 19th Century influenced these events.
📄 Study AP European History, Unit 6: Industrialization and Its Effects
📄 Study AP European History, Unit 7: 19th-Century Perspectives and Political Developments
Two World Wars dominated 💪 European history in the first half of the 20th Century.
World War I
World War I began in August of 1914 and eventually included most of the continent 🌍 and all of the major powers. This massive conflict caused tremendous suffering and disrupted politics.
Causes
Historians often distinguish between long- and short-term causes of World War I. Long-term causes raised tensions between European powers: nationalism, militarism, imperialism, and competing alliances. In the 1910s, conflicts in the Balkans (culminating in the assassination 🔫 of Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand) ignited the Great War, aka World War I, in 1914. Two alliances, the Allies and the Central Powers, fought for over four years.
| Allied Powers | Central Powers |
| Russia (exited early) | Austria-Hungary |
| France | Germany |
| Great Britain | Ottoman Empire |
| Italy (joined late) | |
| US (joined late) |
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Causes of World War I
Effects
New military technologies created horrible conditions and enormous casualties. It is estimated that over 16 million people died over that incident. Warring nations mobilized (actively involved) their populations in Europe and their colonies, conceiving total war. The war deeply affected civilians. The strain of total war led to rebellions and revolutions.
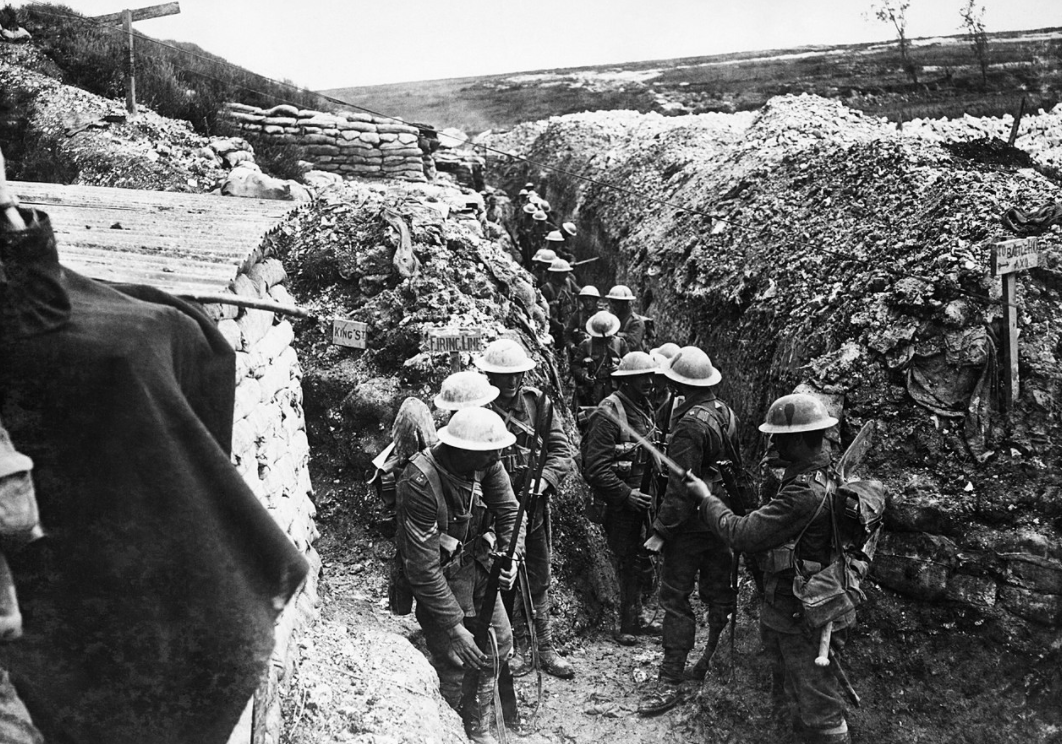

British troops participating in trench warfare
European belligerents (fighting countries) exhausted their resources. This shifted the global balance of power toward the United States, in addition to excluding Germany economically and poltiically, which laid the groundwork for World War II.
Peace Settlement after World War I
The victorious Allies disagreed over how to rebuild international relations after the war. The resulting Treaty of Versailles 🤝 was seen as both too harsh–especially by Germans–and too lenient. The Treaty punished Germany but left it intact while also creating the League of Nations. The United States Senate rejected the Treaty to keep the US out of the League, weakening the organization from its beginning.
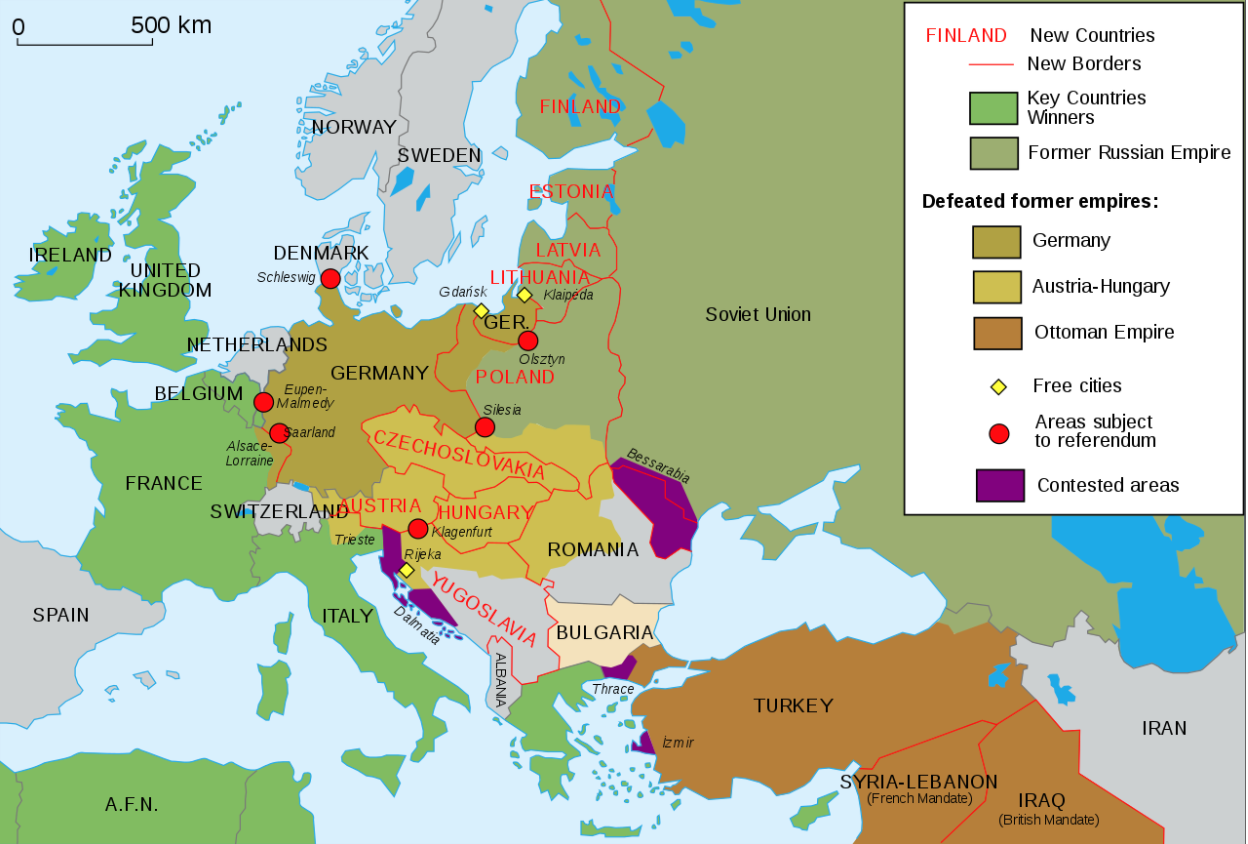
War and revolutions created new countries (1923)
World War I strengthened and weakened European imperialism. Britain, France, and Belgium took control of German colonies and areas of the Ottoman Empire under mandate (authority) from the League of Nations 🌐. But, colonized people in Africa and Asia increased their resistance to imperialism during and after the war.
World War II
In the 1920s and 1930s, Fascist states in Germany and Italy expanded their territory in violation of the Treaty of Versailles, leading to the monumental catastrophe of World War II. Japan joined the Axis powers. Those opposing them were the Allies.
💡Remember: Fascism is an ideology that emphasizes nationalism, authoritarism, and often racism. It first emerged in Italy in the 1920 through the the National Fascist Party of Benito Mussolini.
| Axis Powers | Allied Powers |
| Germany | Great Britain |
| Italy | Free France (continued resisting Germany) |
| Japan | USSR (after initially cooperating with Germany) |
| Vichy France (collaborated with Germany) | China |
| United States (joined later) |
Fighting World War II
Advanced military technology and total warfare made World War II the deadliest war in history. Aerial bombardment 💣 and economic destruction killed millions of civilians. As in the first world war, colonized people mobilized, too.
Initially, the Axis powers conquered vast amounts of territory. The German blitzkrieg (“lightning ⚡️ war” using planes and tanks) overwhelmed most of Europe. Ultimately, the Allies’ combined industrial and technological power overwhelmed and crushed the Axis, reducing German and Italian cities to smoldering piles of rubble.
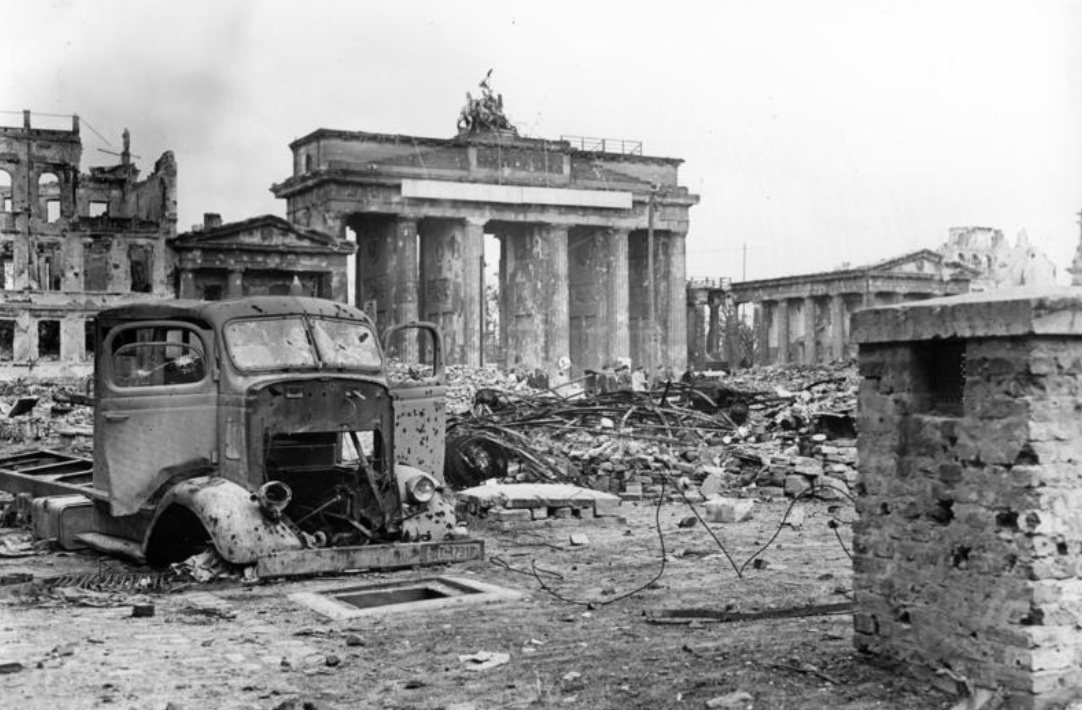

Berlin, Germany, 1945
The Holocaust
Racism, especially anti-Semitism, fueled the Nazi state. Before the war, Nazi Germany created a racial order that oppressed Jews. Under the fog of war, this policy became genocidal as Nazi leaders sought to eliminate European Jewry (all European Jews). During the Holocaust, Nazis and their collaborators murdered millions.
Conflicting Political Ideologies
World Wars and economic collapses 📉 produced new and more extreme political ideologies: communism and fascism.
Communism
The Russian Revolution created the world’s first communist government based on Marxist–Leninist theory. It is based on the idea that everyone should have access to wealth and resources. Communism abolished capitalism and suppressed individual rights for the community’s well-being. The Communist ideology was first developed by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in the mid-19th century.
Russian Revolutions
World War I made a bad situation worse in Russia 🇷🇺. Repressive government and social inequality created support for revolutionary change, and total war exacerbated (made worse) both factors. In 1917, revolutionary workers, peasants, military troops, and intellectuals (that’s a lot of people! 😱) first overthrew the Czar and then the government that replaced the monarchy. Vladimir Lenin’s Bolsheviks took control of the state and created the communist Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, aka the USSR, aka the Soviet Union.
The Soviet State
Lenin’s Bolsheviks renamed themselves the Communist Party. Their state ended capitalism by seizing the means of production (e.g., factories 🏭) and capital (e.g., banks 🏦) from private owners. Initially, Lenin compromised with his communist principles and used limited free-market policies called the New Economic Policy (NEP).
Joseph Stalin took control of the USSR after Lenin and eliminated the NEP with a government-led program of rapid economic modernization. This program built up Soviet industry but at a tremendous cost for Soviet citizens. Stalin also established a powerful dictatorship that did not tolerate any dissent.
Fascism
Ideologies that led to World War I–nationalism and militarism–were the basis for post-war Fascism. Originating in Italy under Benito Mussolini, Fascist movements gained support from nationalists who opposed communism, supported traditional culture, and resisted the post-war settlement. Fascists came to power in Italy in 1922, but their German counterparts Hitler’s Nazi Party only attained political dominance in 1933. Once in power, Mussolini and Hitler ruled as violent dictators 👿.
Global Economic Crisis
The Great Depression began in the United States in 1929 and affected Europe in the 1930s. The financial collapse in the US was the primary cause. Many European banks and businesses depended on US investments 💵 and were rocked by the Depression. The suffering fueled extremist movements, most prominently the rise to power of the Nazi Party in Germany.
Modern Culture
The cultural shock of world wars, economic crises, and political extremism accelerated the questioning of science and rationality that began in the 19th Century. Physics research continued to challenge the idea that the universe 🪐 was predictable while also providing the basis for nuclear weapons and power. Similarly, Freudian psychology, which claimed that subconscious impulses shaped human behavior, gained popularity after World War I. Young people dealing with all of this in the 1920s were sometimes called a “lost generation.”
Similarly, pre- and post-war developments fundamentally altered gender roles. Women publicly mobilized during both World Wars, enhancing their claims to political rights and increasing their economic options. Women’s suffrage groups won the right to vote 🗳 in many European countries, and women became socially freer.

🎥 Watch: AP European History - Rise of Fascism
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🎨Unit 1 – Renaissance & Exploration
⛪️Unit 2 – Reformation
👑Unit 3 – Absolutism & Constitutionalism
🤔Unit 4 – Scientific, Philosophical, & Political Developments
🥖Unit 5 – Conflict, Crisis, & Reaction in the Late 18th Century
🚂Unit 6 – Industrialization & Its Effects
✊Unit 7 – 19th Century Perspectives & Political Developments
💣Unit 8 – 20th Century Global Conflicts
🥶Unit 9 – Cold War & Contemporary Europe
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills
👉Subject Guides

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.