6.4 Effect of Changes in Policies & Economic Conditions on the Foreign Exchange Market
3 min read•november 15, 2020
J
Jeanne Stansak
AP Macroeconomics 💶
99 resourcesSee Units
6.4: Effect of Changes in Policies and Economic Conditions on the Foreign Exchange Market
Change in Demand or Supply in Currency
There are four determinants that can change either the supply or demand in the FOREX Market. These include:

Let's look at some scenarios that fall into these different determinants and see how they affect the various currencies.
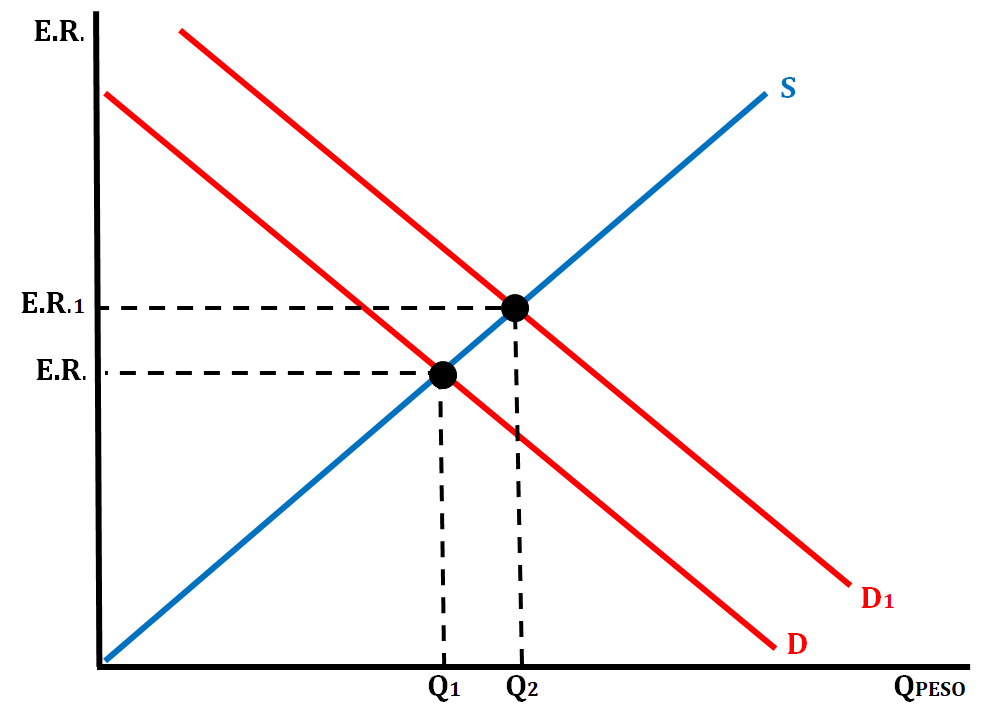
- Scenario # 1: Tourists from all over the world travel to Mexico for Vacation.
- The demand for the peso will increase and the peso will appreciate.
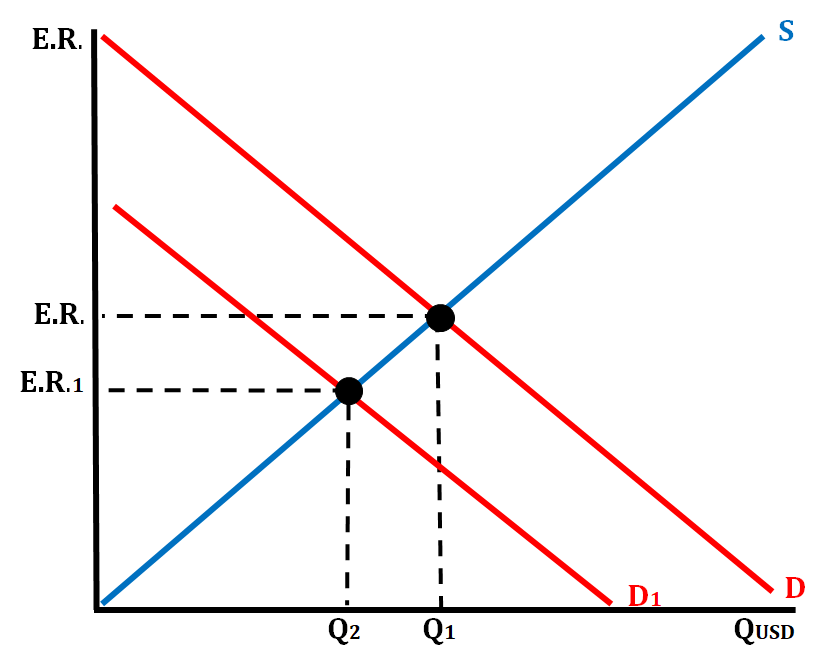
- Scenario # 2: The price of U.S. exports increase. How would this affect the demand for the U.S. dollar?
- It would cause the demand for U.S. goods to decrease which would cause the demand for the dollar to decrease. The U.S. Dollar would depreciate.
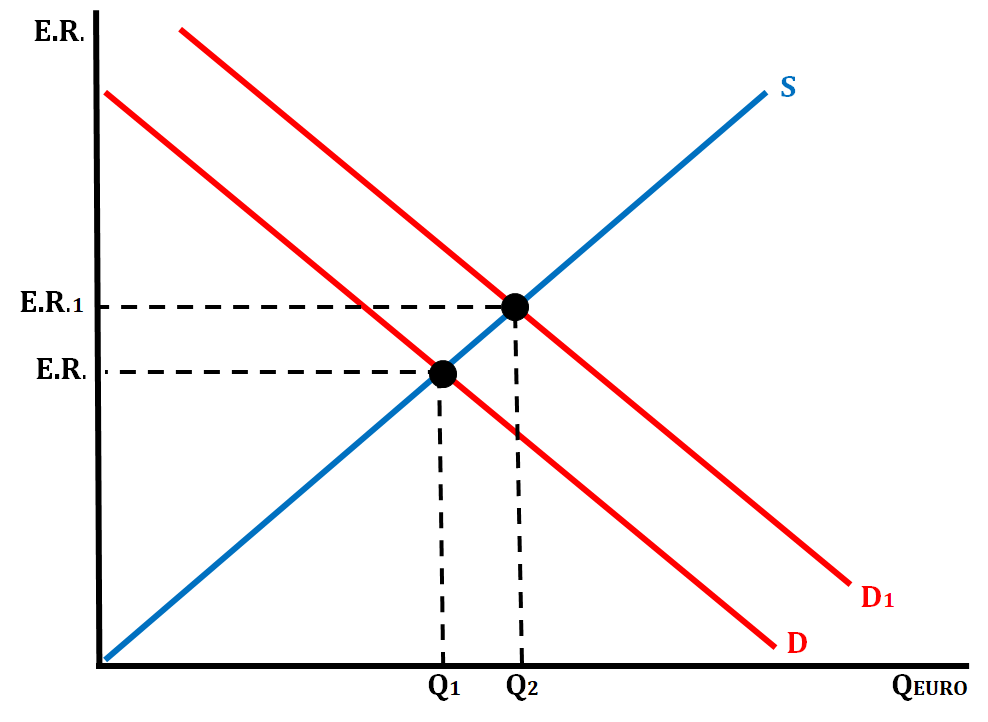
- Scenario # 3: An economic boom causes income levels to increase for Chinese consumers causing them to increase their demand for Germany goods.
- The demand for the Euro will increase, as they need to convert the Yen to Euros. The Euro will appreciate.
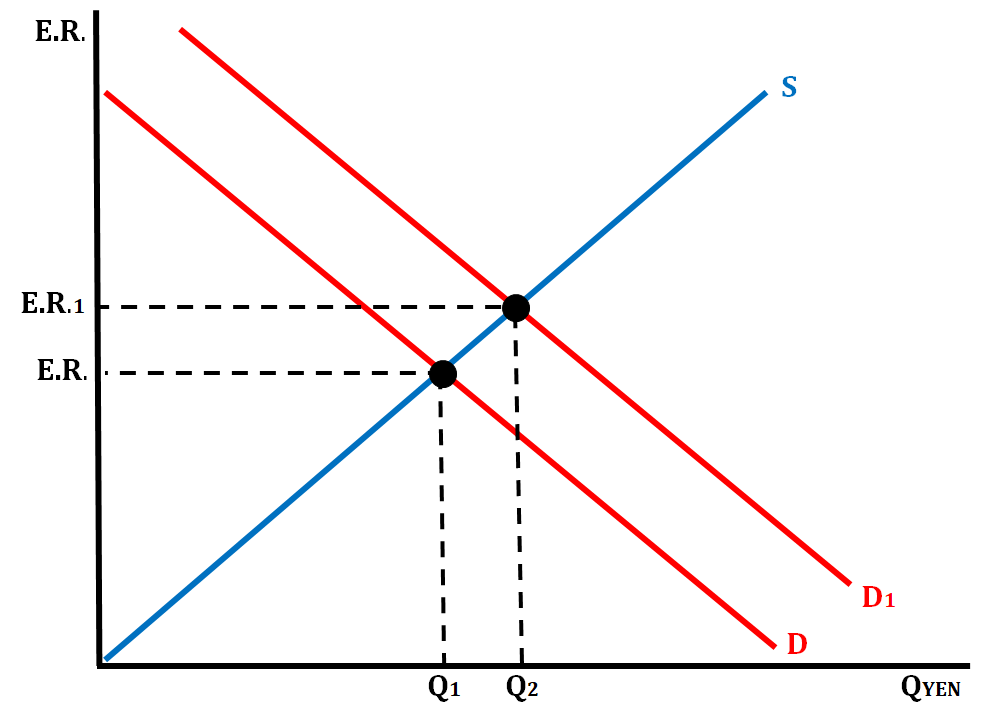
- Scenario # 4: Japanese real interest rates are higher than interest rates in the United States.
- The demand for the Yen will increase and the Yen will appreciate.
Fiscal Policy Impact on Exchange Rates
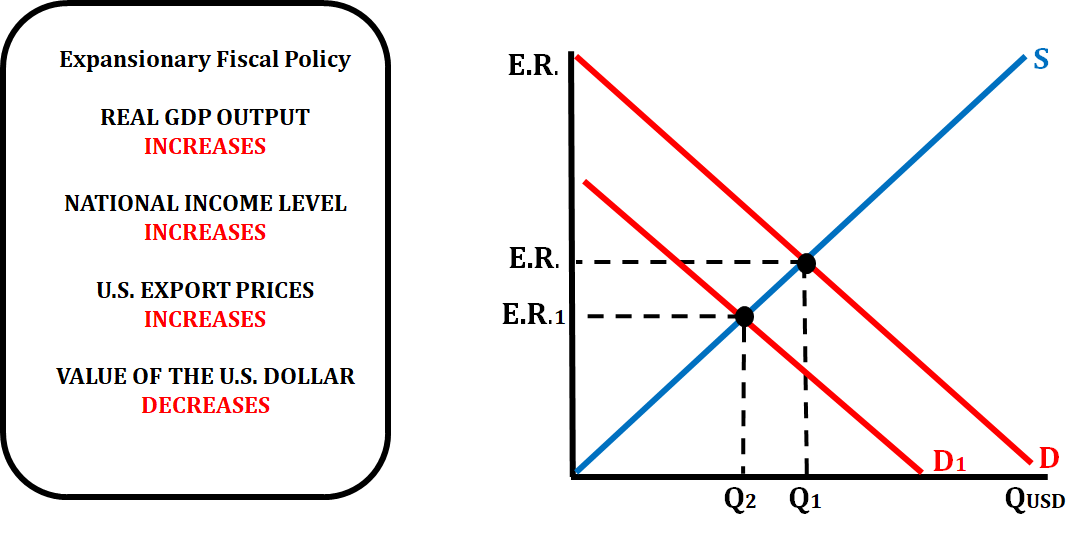
When the government practices an expansionary fiscal policy (increase in spending or decrease in taxes), there is an effect on the exchange rate for that country's currency. The example below shows what would happen if this occurs in the United States.
If the government increases spending or decreases taxes, aggregate demand (AD) will increase, which will increase real GDP output and increase the price level. This makes U.S. goods more expensive which means that other countries will not buy as much. So, there will be less of a demand for the U.S. dollar which will depreciate it.
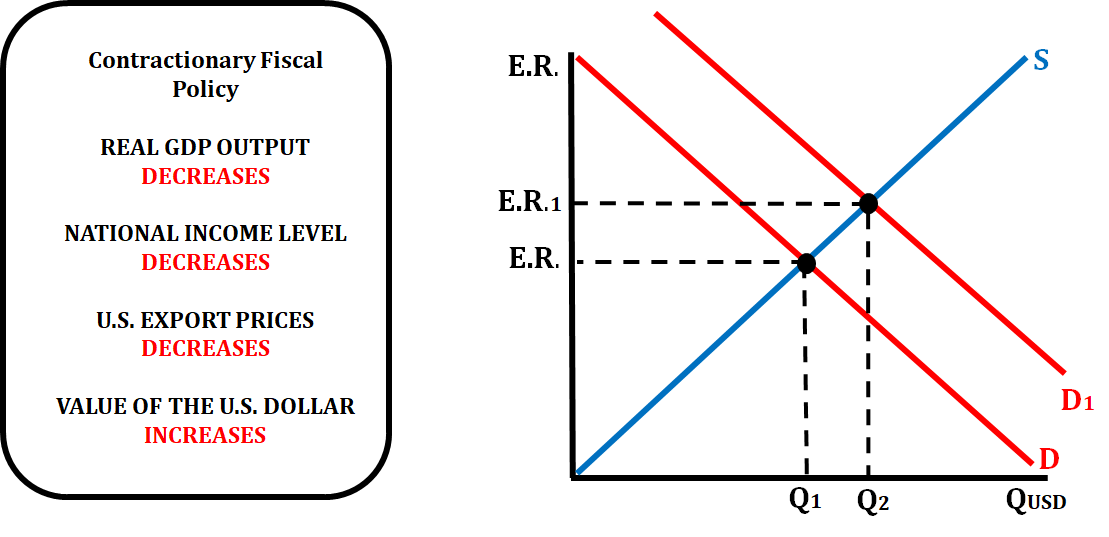
When the government practices a contractionary fiscal policy (decreases spending or increases taxes), there is an effect on the exchange rate of that country's currency. The example below shows what would happen if this occurs in the United States.
If the government either decreases spending or increases taxes, that will decrease aggregate demand which will decrease real GDP output and decrease price level. This will make U.S. goods less expensive which will make them more attractive to foreign consumers. Foreign consumers will increase their purchases of U.S. goods and will need to exchange their currency for the dollar which will increase the demand for the dollar. When the demand for the dollar increases, the value of the dollar will appreciate.
Monetary Policy Impact on Exchange Rates
If the central bank of a country is practicing an expansionary monetary policy (decreasing the reserve ratio, decreasing the discount rate, or buy bonds) it will have an effect on the exchange rate as well. In the following example, we are looking at the actions of the Federal Reserve in the United States.
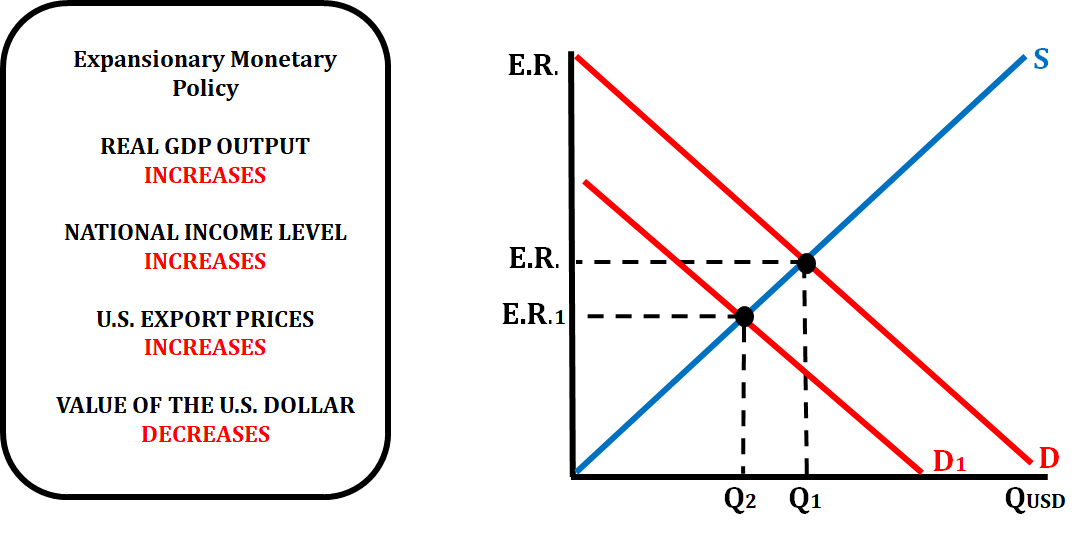
When the FED increases the money supply, that lowers the interest rate which will increase investment spending. When investment spending increases, aggregate demand increases which raises the price level. This means that both the national income levels and export prices will increase. With the U.S. good at higher prices, foreign customers do not want to buy the goods which will decrease the demand for the U.S. dollar, causing a depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
If the central bank of a country is practicing a contractionary monetary policy (increasing the reserve ratio, increasing the discount rate, or selling bonds), it will have an effect on the value of the exchange rate. In the following example, we are looking at the actions of the Federal Reserve in the United States.
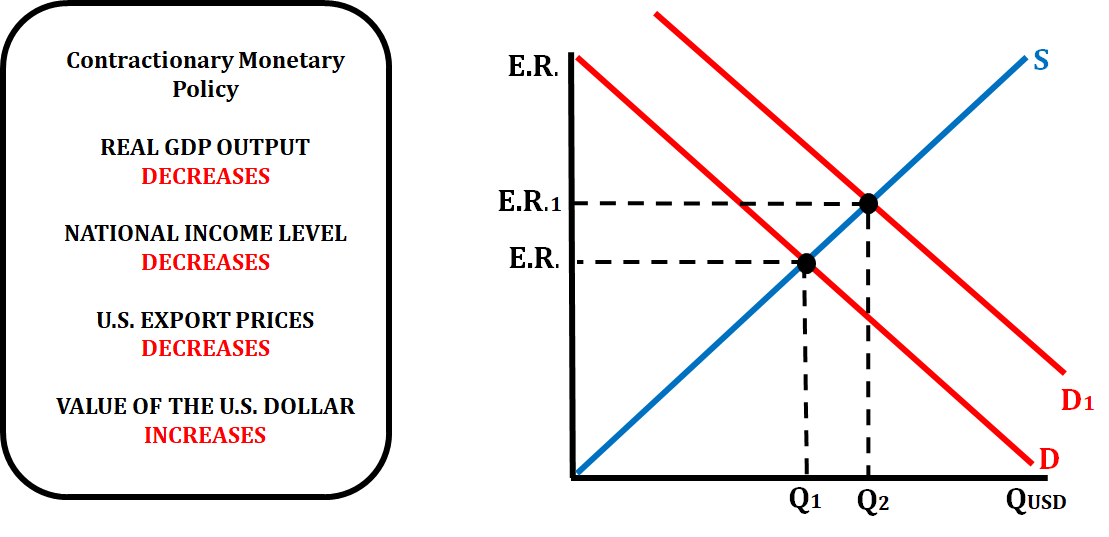
When the FED decreases the money supply, that raises the interest rate which will decrease investment spending. When investment spending decreases, aggregate demand decreases which lower the price level. This means that both the national income levels and export prices will decrease. With the U.S. goods at lower prices, foreign customers want to buy the goods which will increase the demand for the U.S. dollar, causing an appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
💸Unit 1 – Basic Economic Concepts
📈Unit 2 – Economic Indicators & the Business Cycle
💲Unit 3 – National Income & Price Determination
💰Unit 4 – Financial Sector
⚖️Unit 5 – Long-Run Consequences of Stabilization Policies
🏗Unit 6 – Open Economy - International Trade & Finance
📝Exam Skills: MCQ/FRQ

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.