9.5 Calls for Reform and Responses after 1900
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Natalie Pineda
Harrison Burnside
dylan_black_2025
AP World History: Modern 🌍
577 resourcesSee Units
Introduction
On June 4, 1989, the world watched in shock as Chinese troops violently suppressed pro-democracy protests in Tiananmen Square, Beijing. The incident, which left hundreds, possibly thousands, of people dead and injured, sent shockwaves around the world and shone a spotlight on the Chinese government's human rights abuses. As a student, you are no doubt aware of the many ways in which human rights have been shaped and contested throughout history.
This study guide is dedicated to helping you gain a deeper understanding of this complex and important topic, as we explore the rich and varied history of human rights in the global age, from the early 20th century to the present day. Whether you are preparing for an exam or simply seeking to broaden your knowledge, this guide is here to support you every step of the way. Let's get started!

Human Rights in the Global Age 🌎
Humans all around the world began to question governments and the inequitable systems set in place. 1900—present is known as the Global Age because of the interconnectedness of the world through technology and media. Human rights issues which were once limited to the span of one region were now on display for millions to see and hear via radio or television 📺 More groups of people became literate and became involved in politics and professions. Marginalized groups began to protest and advocate for reforms within their communities, which were often oppressed by the government. These groups challenged assumptions about race, gender, and religion.
Human Rights in China
Native Chinese citizens experienced different violations of human rights under communist ruler Mao Zedong. Nationalist Chinese forces under Chiang-Kai Shek fought with the communist forces in the Chinese Civil War in an effort to unite and consolidate power in China. After communist victory in the Chinese Civil War, Mao established a communist government in China in 1949. The Chinese Communist Party then established the People’s Republic of China.
Under this regime, many Chinese citizens were stripped of their human rights, and some were even executed. Here are some of the things that happened under the Chinese Communist Party:
- Land Redistribution: Chinese landowners were terrorized, executed, and stripped of their land. This land was then distributed to the peasant communities of China. Mao Zedong estimated 2 to 3 million Chinese were murdered.
- Re-education Camps: Labor-based camps which were established from 1957-2013. These camps were an extreme punishment to Chinese who broke the law or opposed the government. The people in these camps often faced starvation and lived in scarce conditions. In its later stages it was used solely to punish criminals.
- Great Leap Forward: Communist plan to reform China from an agrarian society to a communist society.
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights is a document that was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on December 10, 1948. The document consists of 30 articles that outline the fundamental rights that every person is entitled to, regardless of their race, religion, nationality, or any other status.
The Declaration states that all human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights, and that everyone has the right to life, liberty, and security of person. It also states that everyone has the right to education, work, and to participate in the cultural life of their community.
In addition, the Declaration prohibits discrimination on any grounds, and guarantees the right to an effective remedy for any violations of one's rights. It also affirms the right to freedom of thought, conscience, and religion, and the right to freedom of opinion and expression.
The Declaration has been widely accepted as a fundamental document on human rights, and has served as the basis for a number of international human rights instruments, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.

Gender Equality
Women and LGBTQ+ communities began to speak out against inequalities in job opportunities, voting, and participation in politics. Women were previously denied educational opportunities; however, rates of literacy increased exponentially during the 1900s—present. This led to protests against suppressive systems that restricted voting from women.
Women got suffrage, or the right to vote, around the globe at different times: United States in 1920, Brazil in 1932, Turkey in 1934, Japan in 1945, and India in 1947. Remember that you don't need to know all these exact dates, but you should have a general idea of the time period!
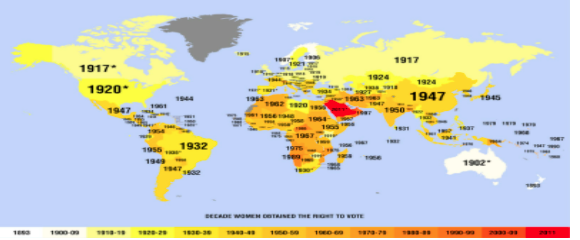
This image is provided by reddit.com, and demonstrates the timeline of women's suffrage across the world in the 1900s.
Civil Rights
Civil Rights Movement in the United States
In the United States, African Americans were discriminated against after emancipation through a series of laws called Jim Crow Laws. African Americans were considered property of their respective slave owners until Emancipation in 1863. But even after emancipation, many African-American citizens continued to be discriminated against. Jim Crow Laws kept society segregated by race and inhibited African Americans from progressing politically and economically in society. The Civil Rights Movement was a series of protests trying to desegregate society and provide equality for all citizens, regardless of skin color ✊🏽✊🏿✊🏻
Some key leaders:
- Martin Luther King Jr, Rosa Parks, Daisy Bates, Betty Friedman, Malcolm X, and countless others.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was passed in order to prohibit discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
Apartheid in South Africa
Apartheid was a system in South Africa that segregated non-white citizens who had to live in a seperate area and use separate facilities. In 1948, the Afrikaner National Party took power and instituted apartheid, which literally means “apartness.” Nelson Mendela was arrested from 1963 to 1990 because of his involvement in Anti-Apartheid movements. The United Nations imposed an embargo on South Africa, and the mounting pressure by the media caused F.W. De Klerk to free Nelson Mandela and end Apartheid. In 1994, a new constitution was written. It ended Apartheid and Nelson Mandela became President of South Africa.

Australian Aborigine Civil Rights Movement
Before European colonization, the native Australian Aborigine population was the majority, but by the 1920s there were only 60,000 Aborigine living in Australia. The Aborigine native population was segregated from society and had no contact with most Australians.
The Western Australia Aborigines Act placed heavy restrictions on natives, gave the government permission to separate children from their parents, and made natives need permission to get a job. This act was, unfortunately, an effort to eradicate the Aborigine population.
The Racial Discrimination Act of 1975 made discrimination against indigineous Aborigine illegal. This was a huge victory for indiginous Aborigine, and in 2008 the Prime Minister, Kevin Rudd, addressed the country in an apology to the indiginous population of Australia for the mistreatments they endured since colonization.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🐎Unit 1 – The Global Tapestry, 1200-1450
🐫Unit 2 – Networks of Exchange, 1200-1450
🕌Unit 3 – Land-Based Empires, 1450-1750
🍕Unit 4 – Transoceanic Interactions, 1450-1750
✊🏽Unit 5 – Revolutions, 1750-1900
🚂Unit 6 – Consequences of Industrialization, 1750-1900
💣Unit 7 – Global Conflict, 1900-Present
🥶Unit 8 – Cold War & Decolonization, 1900-Present
✈️Unit 9 – Globalization, 1900-Present
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
🤔Exam Skills
👉🏼Subject Guides
📝AMSCO Notes

Fiveable
Resources
© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.