5.11 Catalysts and their Effect on Mechanisms
2 min read•april 29, 2020
Jacob Jeffries
AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
🎥 Watch: Catalysis
What is a Catalyst?
Catalysts lower the activation energy of a reaction. Those who are proficient in biology may recognize this as having a similar function as enzymes. Catalysts are defined as species that are consumed in one step in a reaction mechanism but appear again later. Essentially, they go in as a reactant, but come out as a product COMPLETELY UNTOUCHED. They do not play a role in the actual reaction, but rather they modify the mechanism such that the energy regarding the reaction changes. This is shown through the notation of a catalyst being above the reaction arrow as seen in the following image.
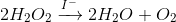
This can be read as "The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen is catalyzed by iodide". The reaction is typically done with potassium iodide, though the iodide ion is the catalyst.

GIF Courtesy of GIPHY
This GIF shown is the reaction that we just described. H2O2 actually decomposes slowly no matter what (As we'll see later, there are two mechanisms, one with and one without a catalyst), but when we add a catalyst, the reaction speeds up like crazy, leading to the "Elephant's Toothpaste" reaction.
Catalysts and Energy
As we saw earlier, a catalyst functions by lowering the Ea (activation energy) for a reaction. Let's take a look at how this works graphically:
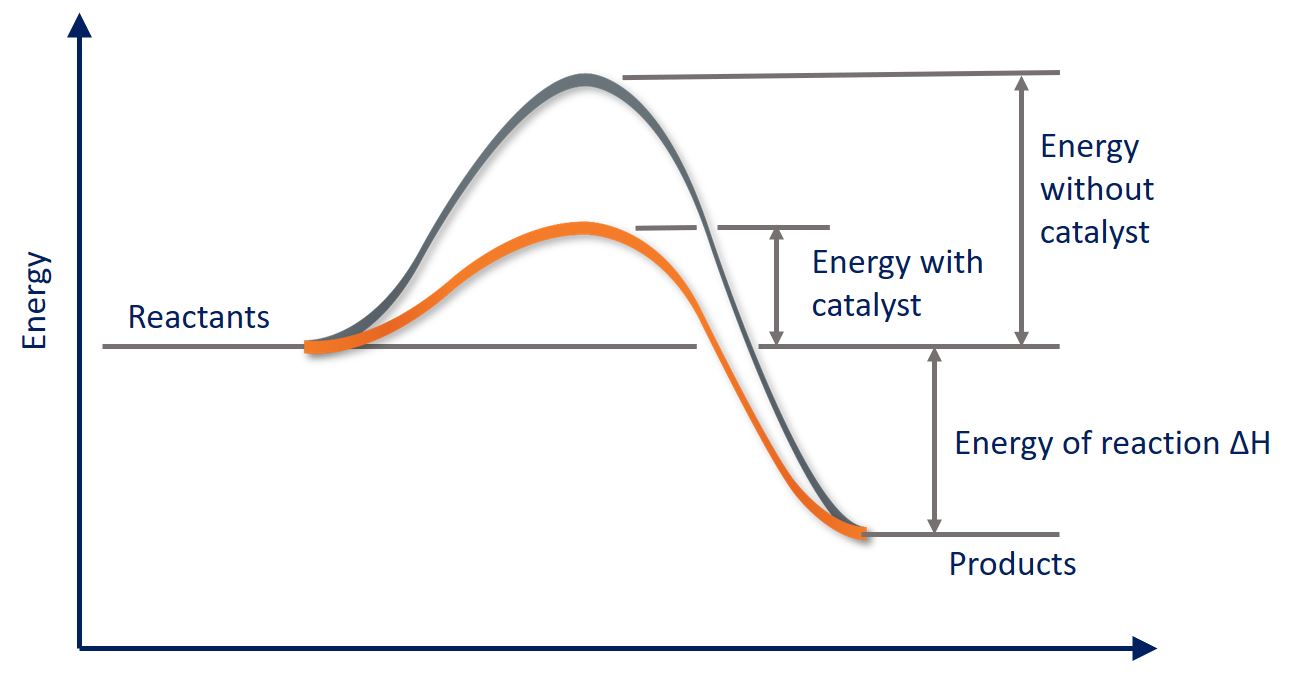
We know that the activation energy is the energy between the reactants and the activated complex (the hump), so then as you can see, catalysts bring down that hump to lower the activation energy. Catalysts may also split a one step high Ea into a multi-step low Ea reaction:
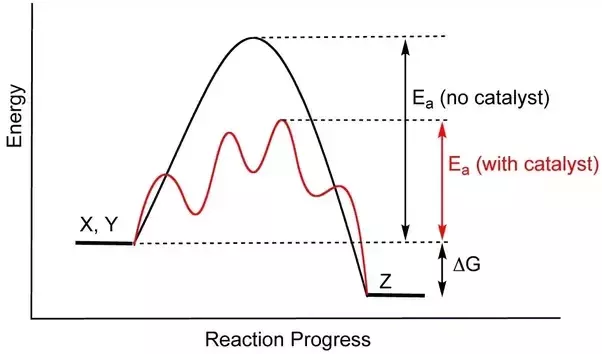
Image Courtesy of Quora
Catalysts and Mechanisms
Though less important to know than the thermodynamic effects, catalysts also change the way a mechanism works. We can see this in two mechanisms for the decomposition of H2O2, one being catalyzed and the other not being catalyzed.
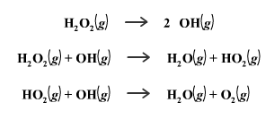
Non-catalyzed Mechanism

Catalyzed Mechanism
The catalyzed mechanism has 2 steps, whereas the uncatalyzed mechanism has 3 steps. This makes the reaction quicker.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
✍️Free Response Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.