2.1 The Influence of Language and Culture on Identity
3 min read•january 13, 2023
Katelyn Lien
AP Japanese 🇯🇵
28 resourcesSee Units
Unit 2 Overview
🗣️ In this unit, you will look at how the Japanese language and culture affect personal and public identities. You will learn more about the Japanese language itself and cultural aspects that will provide more context for the topics you will learn throughout the course. Here are some guiding questions to help get you thinking for this unit:
- How does language affect one's identity?
- What are some different ways you like to greet others?
- Can one's personal and public identities differ? How?
🎌 Japanese Language
Nihongo (日本語)
When someone talks in Japanese, they are speaking nihongo (日本語). Just like people who speak English use certain words that are only used in their areas, Japanese people use a different dialect depending on where they're from. The dialect, or type, of Japanese spoken in a person's town or region, is called hōgen (方言). There are slight variations depending on the region, and it is sometimes difficult to understand. When listening to someone speak a different dialect, you can immediately notice the unique nuances, just like when listening to someone with a Southern or British accent.
The form of Japanese that is taught in school and is spoken by most people around Tokyo is hyōjungo (標準語). In the 1800s, after the Meiji Restoration, Tokyo, the capital of Japan, imposed this dialect to unite all Japanese people. In the past, people learned to speak hyōjungo so they could move to the city and get a job. Even now, some people must switch from hōgen to hyōjungo. Hyōjungo is now considered the "Standard Japanese," and all textbooks and teachers use this dialect.

Image Courtesy of Free SVG
🔠 Japanese Alphabet
Japanese consists of three main alphabets: kanji (漢字), hiragana (ひらがな), and katakana (カタカナ).
Kanji (漢字)
- First developed in China and was gradually used by Japanese people
- Created from pictograms
- Ex: the kanji for tree is 木 which is supposed to resemble a tree
- when two 木 are written together, it becomes 林, which means forest
- Most Kanji from China can be read in the on yomi (音読み), which is the Chinese way of reading, or the kun yomi (くん読み), the Japanese reading
- Each year starting in first grade, students must learn a certain number of kanji and have kanji tests regularly
Hiragana (ひらがな)
- Phonetic Japanese alphabet
- Each character represents one syllable
- 46 characters
- The first of the three alphabets taught at school
- Most kids can read and write hiragana before they enter school

Image Courtesy of Japanese with Anime
Katakana (カタカナ)
- Phonetic alphabet used to write foreign words
- Each character represents one syllable
- 46 characters, just like hiragana
- Ex: orange is オレンジ, which is read as "o-ren-ji"
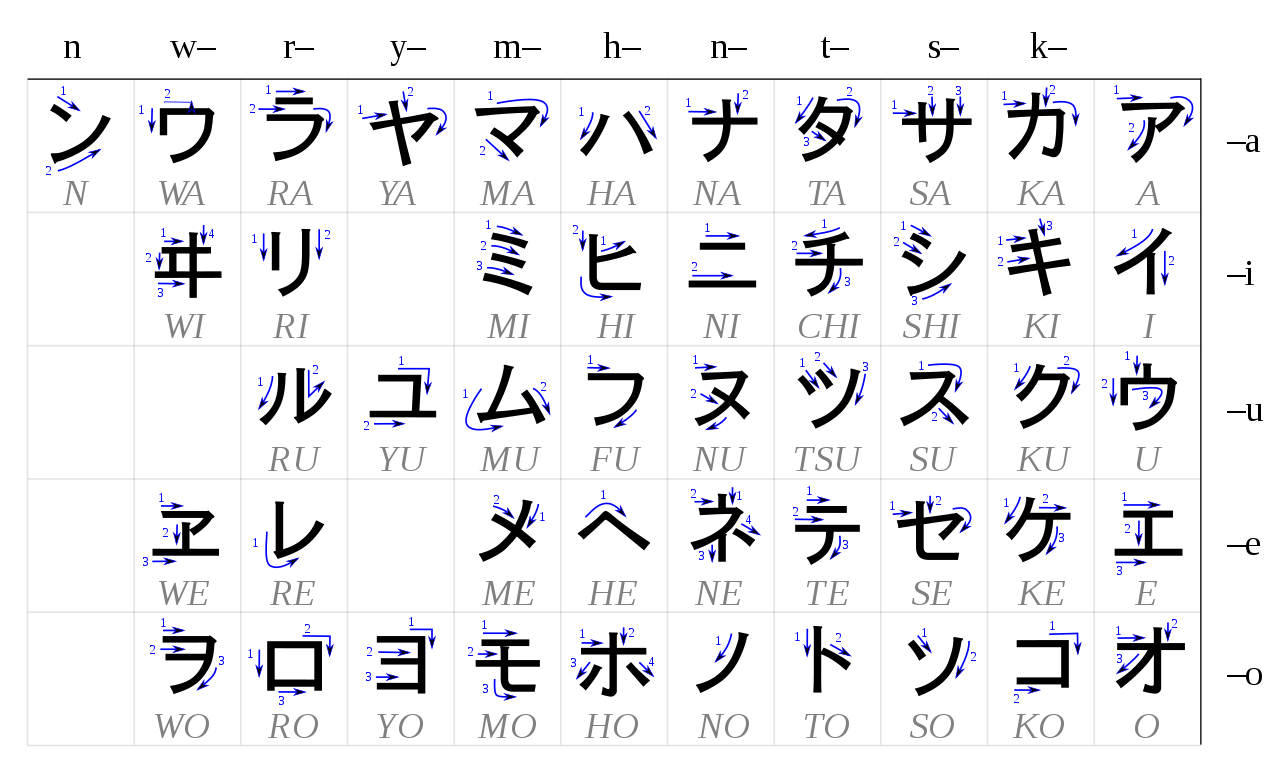
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia
🔑 Key Words
- Nihongo (日本語): Japanese
- Hōgen (方言): Dialect
- Hyōjungo (標準語): Japanese dialect spoken around Tokyo
- Kanji (漢字): Japanese alphabet consisting of characters derived from pictograms
- Hiragana (ひらがな): Phonetic alphabet
- Katakana (カタカナ): Phonetic alphabet for foreign words
- On yomi (音読み): Chinese reading
- Kun yomi (くん読み): Japanese reading
- Ki (木): Tree
- Hayashi (林): Forest
💥 Strive for a Five Vocabulary
- Gakkō (学校): school
- Gakunen (学年): grade level
- Kotoba (言葉): word
- Gengo (言語): language
- Gaikokugo (外国語): foreign language
- Hon (本): book
- Oboeru (覚える): to learn
- Oshieru (教える): to teach
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👨👩👧Unit 1 – Families in Japan
🗣Unit 2 – Language & Culture in Japan
🎨Unit 3 – Beauty & Art in Japan
🔬Unit 4 – Science & Technology in Japan
🏠Unit 5 – Quality of Life in Japan
💸Unit 6 – Challenges in Japan
✍️Exam Skills - FRQ/MCQ

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.