Victoria Sokol
AP Spanish Language 🇪🇸
54 resourcesSee Units
The language you speak is inherently connected to your culture and your personal identity. A group of people that all speak the same language or even the same dialect of the language have their own unique collective identity. In the following subsections, we will explore a few of the most predominant minority languages that exist in the Spanish-speaking world and some of their influences on the majority group.
Minority Languages in Spain
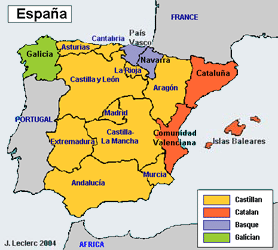
Image from Antioch Culture Conflict.
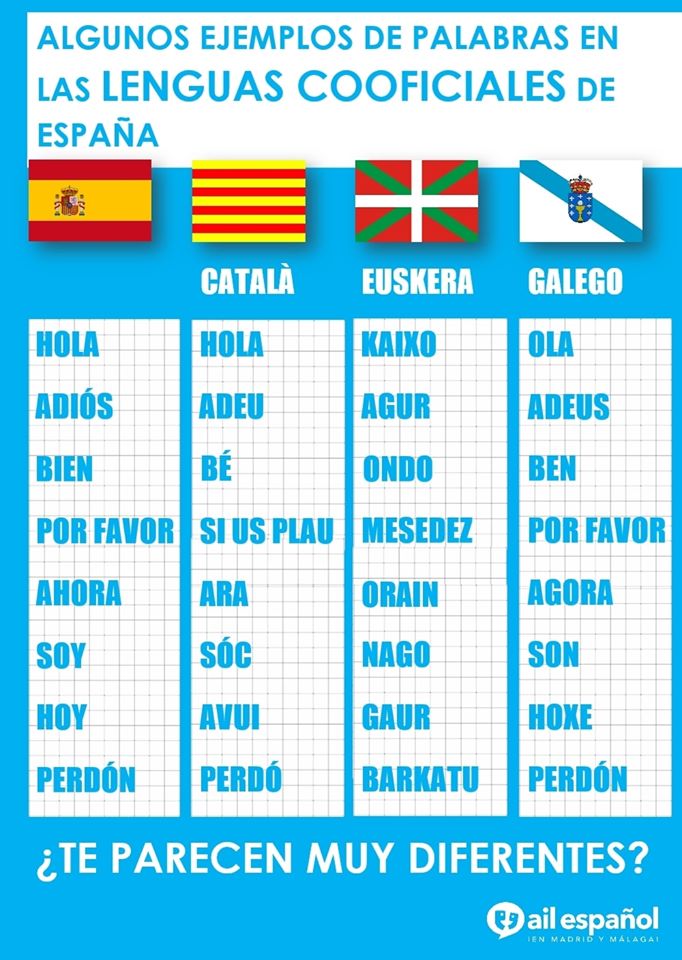
In Spain, there are three co-official languages recognized in addition to Castilian Spanish. Each is used in a different region of the country.
Catalan/Català & Valencian/Valencià
Catalan and Valencian are considered the same language, just spoken in different autonomous communities. Catalan is a romance language (meaning it has roots from Latin) that first appeared somewhere in the 10th or 11th century. It went through a period of repression by the monarchy that tried to keep uniformity across the empire, but was reborn during the Renaissance in strength and use. Now, it is a co-official language in Cataluña and Las Islas Baleares with over 9.5 million speakers. Catalan is widely taught in schools so many locals are bilingual as a result. Data from the 2011 census shows 73% of the locals speak Catalan in Cataluña, 95% understand it, 56% can write it. It is used in the media and in official government documents. In Cataluña, the language is evident in road names, local businesses and historical landmarks like La Sagrada Família.
Galician/Gallego
Galician is also a romance language and started in the 9th century. It seems like a mixture of Castilian Spanish and Portuguese because of its location. During Francisco Franco's dictatorship from 1939 to 1975, many of the minority languages were prohibited. After his death, Galician (along with the other minority languages) were revived. Nowadays, there are more than 2 million speakers of Galician.
Basque/Euskera
One would think the location of País Vasco, being so close to France, would influence the Basque language to be like a mixture of French and Spanish, but the Basque language is considered an enigma. Linguistically, it has no connection to either language! Some believe it is one of the only surviving indigenous languages of the Iberian peninsula before the Romance languages were introduced to the area. Because of its age, there is little known about the origin of the language. There are very few overlapping words between Castilian Spanish and the Basque language. Because geographically, the Basque region is smaller and a lower percentage of the autonomous community's population actively speaks Basque, the number of speakers throughout history has been less than the aforementioned minority languages; today there are only around 1 million native speakers. Inside of País Vasco, many public signs are written or labeled in both Castilian and Basque because there is a local pride and continued push for reviving more bilingual speakers.
El Silbo Gomero
¡El silbo gomero es una lengua muy única! Solo se encuentra en la Isla de la Gomera en Las Islas Canarias. Se comunica con silbidos tonales que pueden transferir por las distancias en las montañas de la isla. Aunque muchas personas en la isla entienden, está desapareciendo porque los "hablantes" nativos son mayores y se aprende en casa. Las personas que nacieron entre 1950 y 1980 casi no aprendieron y son incapaces de usarla. UNESCO ha documentado un revitalización de la lengua, y ahora los niños de la isla pueden aprenderla formalmente.
Minority Languages in Central & South America
There are over 600 indigenous languages spoken in Central and South America. Many of these are endangered.

The Náhuatl language originated in present day southern México and was used by the Mesoamerican Mexica civilization (AKA Aztecs). Since this civilization dominated the region for centuries, the number and geographic coverage of the population kept the language strong until the introduction of Spanish by the conquistadores in the 15th century. Before the arrival of the Spanish, the written language was mostly pictograms and ideograms. The Spanish used the Latin script to write down what they heard the Mexica saying, so some spellings are subjective. Nowadays, there are approximately 1.5 million speakers of Náhuatl.
Palabras En Español de Náhuatl
| Náhuatal | Español | Definición |
| izquitl | esquite | botana de maíz |
| apapachoa | apapachar | palmada cariñosa a la cara |
| ahuacatl | aguacate | verdura verde usada para hacer guacamole |
| xocolātl | chocolate | dulce hecho de manteca de cacao y azúcar |
| comalli | comal | sartén usada para cocer tortillas |
| tiyānquiztli | tianguis | tipo de mercado en México |
| tomatl | tomate | verdura roja y jugosa usada para hacer salsa |
| tzictli | chicle | goma para masticar |
Guaraní
The Guaraní language is native to Paraguay, Bolivia, Argentina and Brazil and is an official language of Paraguay where a majority of the population speaks it along with Spanish. It is a point of pride for many Paraguayans and throughout history has been used as a mode of communication to distinguish locals from their enemies.
Palabras En Español del Guaraní
| Guaraní | Español | Definición |
| naná naná | ananá | en algunas partes la fruta amarilla piña=ananá |
| jaguarete | jaguar | animal felino con manchas |
| maracuyá | maracuyá | fruta con pulpa amarilla y muchas semillas |
| pira aña | piraña | pez de los ríos con muchos dientes y es carnívoro y feroz |
| ĩwasaʼi | açai | fruta pequeña con pulpa jugosa con muchos antioxidantes |
Quechua
Quechua is the language of the Incas from the Andean region. Speakers are mostly located in what is now Perú, Bolivia, Ecuador, Colombia and Argentina. It is recognized as an official language in Perú and Bolivia. The language has been alive since before common era. Today, exact numbers of speakers is hard to clarify because some speakers live in remote areas and don't participate in all reporting; the best estimate is over 10 million speakers.
Palabras En Español de Quechua
| Quechua | Español | Definición |
| kancha | cancha | lugar al juego de pelota |
| kuntur | cóndor | ave de carroña grande de la región andina |
| mati | mate | hierba que usa para una infusión |
| kuka | coca | planta con propiedades contra soroche |
| kinwa | quinua | planta con numerosas semillas comestibles |
| allpaqa | alpaca | animal de familia camélido con lana muy fina |
Aymara
Aymara or aimara, is a language spoken in Bolivia, Perú, Chile and Argentina. It has some similarities to quechua possibly because of the overlap in geographic location. There are over 2 million speakers nowadays, but this language is considered threatened because of the decline in number of speakers. Many children are tending to switch to only Spanish because of globalization and social advancement.
Palabras En Español de Aymara
| Aymara | Español | Definición |
| antis | Andes | las montañas en el oeste del continente |
| wawa | guagua | niño o bebé |
| Cuzco | Cusco | ciudad central en el imperio inca |
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👨👩👧Unit 1 – Families in Spanish-Speaking Countries
🗣Unit 2 – Language & Culture in Spanish-Speaking Countries
🎨Unit 3 – Beauty & Art in Spanish-Speaking Countries
🔬Unit 4 – Science & Technology in Spanish-Speaking Countries
🏠Unit 5 – Quality of Life in Spanish-Speaking Countries
💸Unit 6 – Challenges in Spanish-Speaking Countries
🙏Exam Reviews

Fiveable
Resources
© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.